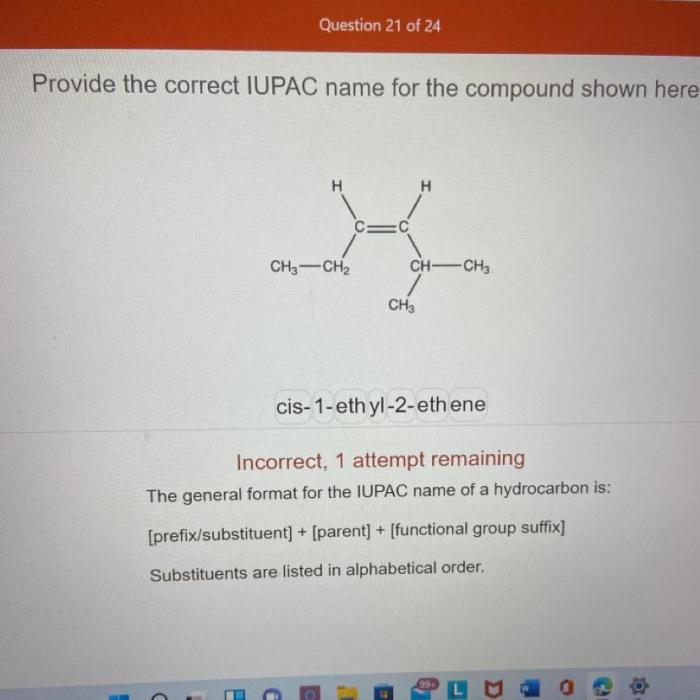
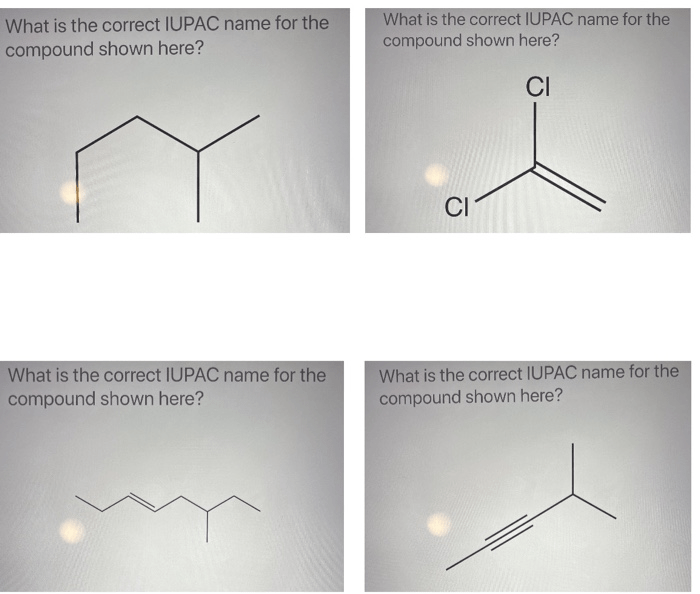
Provide the correct iupac name for the compound shown here – In the realm of chemistry, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature system stands as the cornerstone for naming chemical compounds with precision and clarity. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of IUPAC nomenclature, empowering you to decipher the structure and identity of even the most complex molecules.
Through a systematic approach, we will unravel the rules governing functional group identification, parent chain selection, numbering, substituent naming, and the intricacies of branched and cyclic structures. With each step, you will gain a deeper understanding of the language of chemistry, enabling you to communicate chemical structures with confidence and accuracy.
IUPAC Nomenclature Basics
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature system provides a standardized set of rules for naming chemical compounds. It ensures that compounds are named consistently and unambiguously, facilitating communication and understanding among chemists.
Using IUPAC names is essential for:
- Identifying and classifying compounds
- Predicting their properties and reactivities
- Communicating chemical information accurately
Identifying Functional Groups: Provide The Correct Iupac Name For The Compound Shown Here
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms that give compounds their characteristic chemical properties. They are classified based on their structure and reactivity.
Common functional groups include:
- Alkanes:Contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms, single bonds
- Alkenes:Contain a carbon-carbon double bond
- Alkynes:Contain a carbon-carbon triple bond
- Alcohols:Contain a hydroxyl group (-OH)
- Aldehydes:Contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a hydrogen
- Ketones:Contain a carbonyl group bonded to two carbons
- Carboxylic acids:Contain a carboxyl group (-COOH)
Parent Chain Selection
The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in a molecule. It determines the base name of the compound.
Rules for parent chain selection:
- Select the chain with the most carbon atoms.
- If multiple chains have the same number of carbon atoms, choose the one with the most functional groups.
- If there are still ties, choose the chain with the highest priority functional group.
Numbering the Parent Chain

The parent chain is numbered to assign locants to substituents and functional groups.
Rules for numbering:
- Start numbering from the end of the chain closest to a functional group or multiple bond.
- Assign the lowest locants possible to substituents and functional groups.
- If there is a tie, give priority to the substituent or functional group with the higher atomic number.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of IUPAC nomenclature?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized system for naming chemical compounds, ensuring consistency and clarity in scientific communication.
How do I identify functional groups using IUPAC nomenclature?
Functional groups are identified by their characteristic prefixes and suffixes, which indicate the type and connectivity of atoms within the group.
What are the rules for selecting the parent chain in a molecule?
The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule, and it determines the base name of the compound.