The mitosis and cell cycle double puzzle delves into the intricate dance between mitosis, the process of cell division, and the cell cycle, the sequential stages of cell growth and reproduction. Understanding this interplay is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of cellular life, from the development of organisms to the prevention and treatment of diseases.
Mitosis, a fundamental process in all living organisms, ensures the accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material during cell division. It involves a precisely orchestrated series of stages, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each characterized by distinct chromosomal movements and structural changes.
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
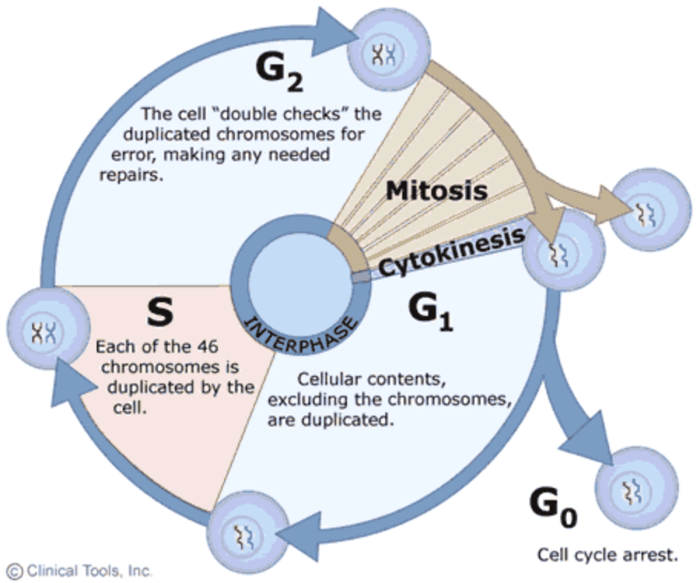
Mitosis is a fundamental process in cell biology that results in the division of a single cell into two genetically identical daughter cells. It plays a critical role in growth, development, and repair of multicellular organisms.
Understanding the relationship between mitosis and the cell cycle is essential for comprehending the fundamental mechanisms that govern cell division and proliferation.
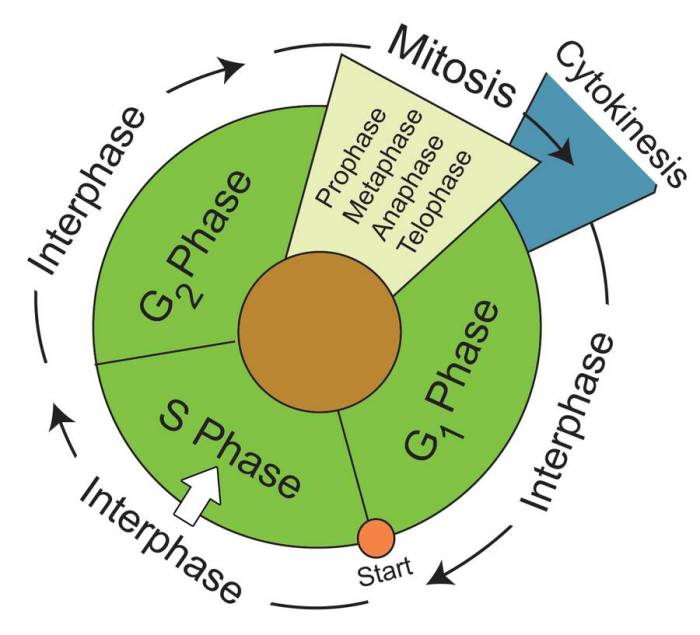
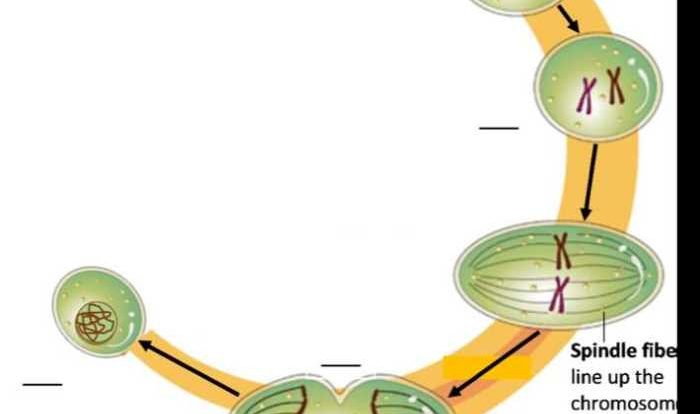
Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis consists of four distinct stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase:Chromosomes become visible, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers form.
- Metaphase:Chromosomes align at the equator of the cell.
- Anaphase:Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase:Two new nuclear envelopes form around the separated chromosomes, and the spindle fibers disappear.
Regulation of Mitosis
Mitosis is tightly regulated by a complex network of proteins and checkpoints.
- Checkpoints:These are control points that ensure that critical events occur correctly before the cell proceeds to the next stage of mitosis.
- Cell Cycle Regulators:Proteins, such as cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), control the timing and progression of mitosis.
- Disruptions in Regulation:Errors in mitosis regulation can lead to genetic abnormalities and diseases, such as cancer.
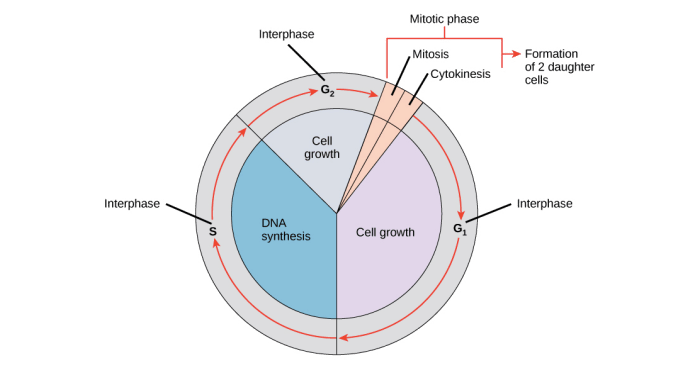
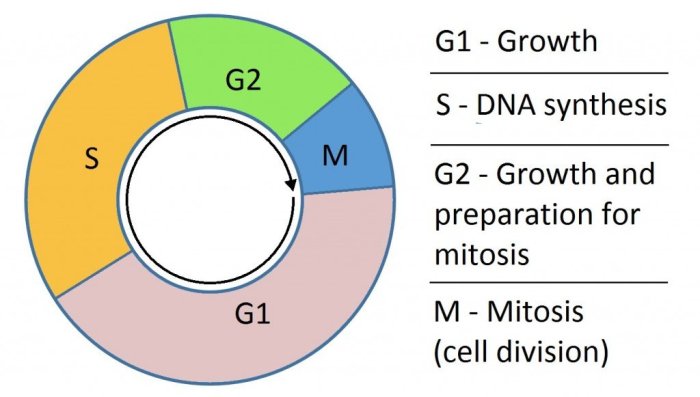
Relationship between Mitosis and the Cell Cycle, Mitosis and cell cycle double puzzle
Mitosis is a key component of the cell cycle, which is the complete sequence of events that a cell undergoes from one division to the next.
- Cell Growth and Development:Mitosis contributes to cell growth by increasing the number of cells in an organism.
- Repair:Mitosis allows damaged cells to be replaced, ensuring the maintenance of healthy tissues.
- Consequences of Errors:Errors in mitosis can result in abnormal cell numbers, genetic instability, and developmental defects.
Applications of Mitosis Research
Understanding mitosis has practical applications in various fields:
- Medicine:Mitosis research helps in understanding and treating diseases like cancer.
- Biotechnology:Mitosis manipulation is used in genetic engineering and cell culture techniques.
- Agriculture:Mitosis regulation knowledge aids in crop improvement and plant breeding.
Question Bank: Mitosis And Cell Cycle Double Puzzle
What is the significance of mitosis?
Mitosis is essential for growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms. It ensures the equal distribution of genetic material to daughter cells, maintaining genetic stability and cellular function.
How is mitosis regulated?
Mitosis is tightly regulated by checkpoints and cell cycle regulators, ensuring that each stage is completed accurately before proceeding to the next. Disruptions in this regulation can lead to genetic instability and diseases.
What are the applications of mitosis research?
Mitosis research has led to advancements in cancer treatment, genetic engineering, and regenerative medicine. Understanding mitosis provides insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic interventions.