Unit 8 polygons and quadrilaterals – Unit 8: Polygons and Quadrilaterals embarks on an enthralling journey into the realm of geometric shapes, where the intricate interplay of sides, angles, and vertices unfolds. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of polygons, exploring their diverse characteristics and properties, before delving deeper into the captivating realm of quadrilaterals, uncovering their unique attributes and relationships.
As we traverse this mathematical landscape, we will unravel the mysteries of these geometric entities, discovering their applications in various fields, from architecture to engineering and design. Prepare to be captivated as we unlock the secrets of polygons and quadrilaterals, revealing their elegance and practical significance.
Polygon Basics
Polygons are closed figures in a plane, formed by straight line segments that connect a finite number of points. These points are called vertices, and the line segments connecting them are called sides. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they have.
Properties of Polygons
- The sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is (n-2) – 180 degrees.
- The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees.
- Polygons with an even number of sides can be divided into two equal parts by a diagonal that connects two non-adjacent vertices.
- Polygons with an odd number of sides cannot be divided into two equal parts by a diagonal.
Common types of polygons include triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), and octagons (8 sides).
Quadrilaterals: Unit 8 Polygons And Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals are polygons with four sides. They are classified into different types based on the properties of their sides and angles.
Types of Quadrilaterals
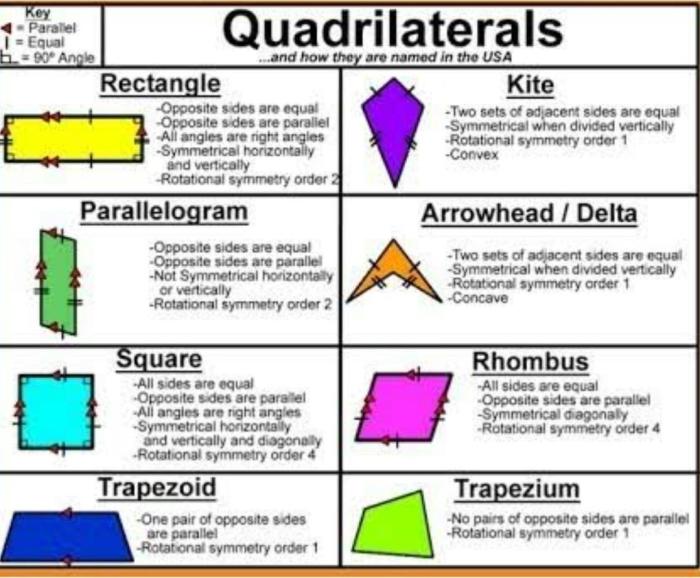
- Square: A quadrilateral with four equal sides and four right angles.
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides and four right angles.
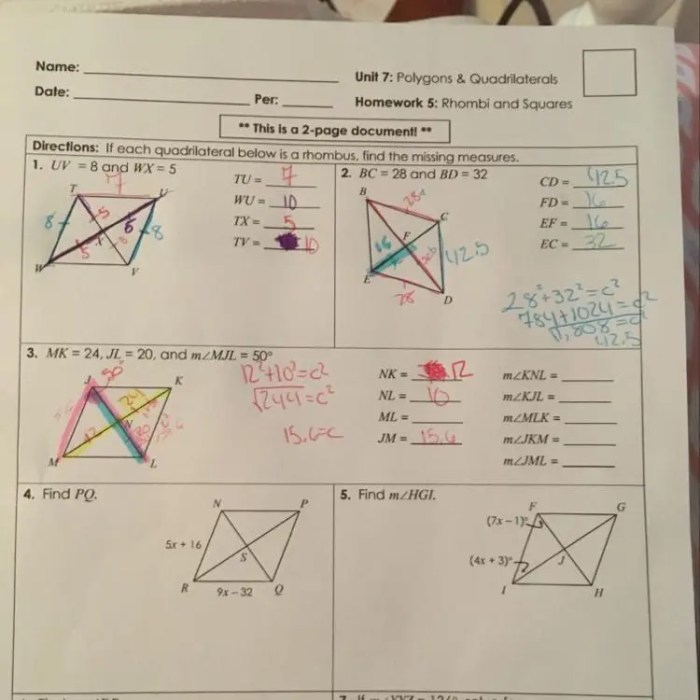
- Rhombus: A quadrilateral with four equal sides but no right angles.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
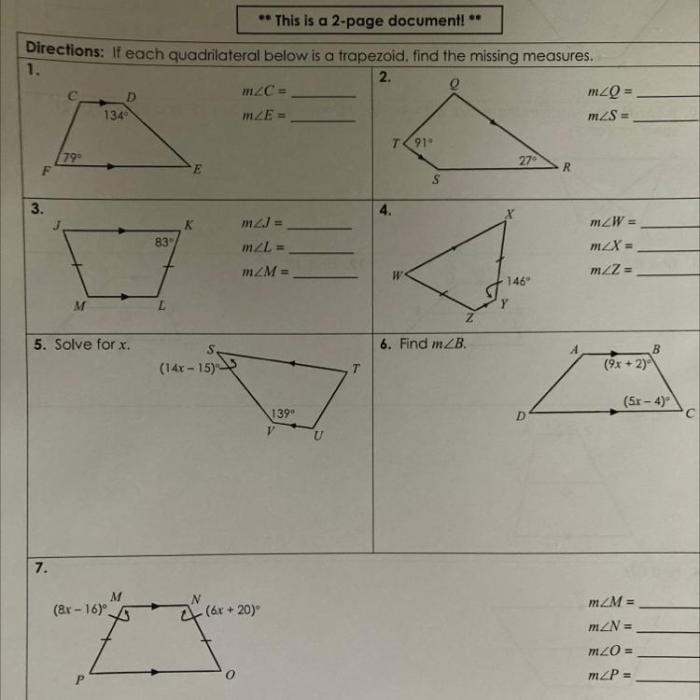
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.
Quadrilaterals have various properties and relationships between their sides and angles, which are discussed in the following sections.
Properties of Quadrilaterals
Opposite Sides and Angles
- In a parallelogram, opposite sides are parallel and equal in length.
- In a rectangle, opposite sides are parallel and equal in length, and opposite angles are equal.
- In a rhombus, opposite sides are parallel and equal in length, and opposite angles are equal.
Diagonals
- Diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
- Diagonals of a rectangle are equal in length and bisect each other.
- Diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other and bisect each other.
Angles and Sides, Unit 8 polygons and quadrilaterals
- The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360 degrees.
- In a parallelogram, opposite angles are equal.
- In a rectangle, all four angles are right angles.
- In a rhombus, all four angles are equal.
Classifying Quadrilaterals
Quadrilaterals can be classified into different types based on their properties. The following table summarizes the key characteristics of different types of quadrilaterals:
| Quadrilateral | Properties |
|---|---|
| Square | Four equal sides, four right angles |
| Rectangle | Two pairs of parallel sides, four right angles |
| Rhombus | Four equal sides, no right angles |
| Parallelogram | Two pairs of parallel sides |
| Trapezoid | One pair of parallel sides |
Real-world examples of quadrilaterals include:
- A square is a picture frame.
- A rectangle is a door.
- A rhombus is a kite.
- A parallelogram is a window.
- A trapezoid is a traffic sign.
Quadrilateral Applications
Quadrilaterals have practical applications in various fields, including:
- Architecture: Quadrilaterals are used in the design of buildings, windows, and doors.
- Engineering: Quadrilaterals are used in the design of bridges, trusses, and other structures.
- Design: Quadrilaterals are used in the design of logos, posters, and other visual elements.
For example, the Golden Gate Bridge is a suspension bridge that uses quadrilaterals in its design. The bridge’s main span is a rectangle, and the towers that support the bridge are parallelograms.
Quadrilateral Relationships
Different types of quadrilaterals have relationships based on their properties.
- All squares are rectangles.
- All rectangles are parallelograms.
- All rhombuses are parallelograms.
This means that a square is the most specific type of quadrilateral, followed by a rectangle, then a rhombus, and finally a parallelogram.
FAQ Compilation
What is a polygon?
A polygon is a closed plane figure with three or more straight sides.
What are the different types of quadrilaterals?
Common types of quadrilaterals include squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites.
What is the relationship between the sides and angles of a quadrilateral?
The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360 degrees.